
The back panel also contains structures and functions which perform operations on controls and supply data to indicators. All of the objects placed on the front panel will appear on the back panel as terminals. The back panel, which is a block diagram, contains the graphical source code. Indicators are outputs: they indicate, or display, the results based on the inputs given to the VI. Controls are inputs: they allow a user to supply information to the VI. The front panel is built using controls and indicators. The last is used to represent the VI in the block diagrams of other, calling VIs. Each VI has three components: a block diagram, a front panel, and a connector pane.
LabVIEW programs-subroutines are termed virtual instruments (VIs). LabVIEW integrates the creation of user interfaces (termed front panels) into the development cycle. : 1–2 Multi-processing and multi-threading hardware is exploited automatically by the built-in scheduler, which multiplexes multiple OS threads over the nodes ready for execution. Since this might be the case for multiple nodes simultaneously, LabVIEW can execute inherently in parallel. These wires propagate variables and any node can execute as soon as all its input data become available. Execution flow is determined by the structure of a graphical block diagram (the LabVIEW-source code) on which the programmer connects different function-nodes by drawing wires.

If there is enough data available to a subVI or function, that subVI or function will execute. The programming paradigm used in LabVIEW, sometimes called G, is based on data availability.
#MATHSCRIPT NODE LABVIEW 2014 FREE#
NI released the free for non-commercial use LabVIEW and LabVIEW NXG Community editions on April 28th, 2020. The latest versions of LabVIEW are LabVIEW 2021 SP1 (released in February 2022) and LabVIEW NXG 5.1 (released in January 2021).
#MATHSCRIPT NODE LABVIEW 2014 WINDOWS#
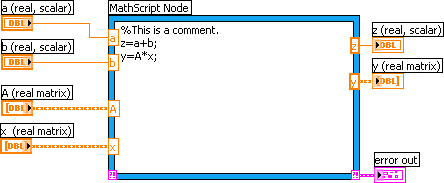
The G dataflow language was originally developed by LabVIEW, LabVIEW is commonly used for data acquisition, instrument control, and industrial automation on a variety of operating systems (OSs), including Microsoft Windows as well as various versions of Unix, Linux, and macOS. The graphical language is named "G" not to be confused with G-code. Laboratory Virtual Instrument Engineering Workbench ( LabVIEW) : 3 is a system-design platform and development environment for a visual programming language from National Instruments. What changes have occurred over previous versions?Īdd links to internal wiki pages that would also help.Īdd links to external resources that would also help.Data acquisition, instrument control, test automation, analysis and signal processing, industrial control, embedded system design Note: The MathScript Node and the LabVIEW MathScript Window can communicate only if they are in the same application instance.Īdd other best practices for this function. When you create a LabVIEW MathScript, you must use supported data types. You also can move the cursor over a function to display information about the function in the Context Help window. To display the data type of a variable in the Context Help window, click outside a MathScript Node and then move the cursor over a variable in the node. You can right-click an output variable to set its data type. Right-click the node border to add input and output variables. Enter your script, which can contain built-in MathScript functions and user-defined functions, in the node or right-click the node border to import text into the node. You can modify your script to remove the warning glyph from the MathScript Node and improve run-time performance. If a MathScript Node contains a warning glyph, LabVIEW operates with slower run-time performance for the node.
You can use the MathScript Node to evaluate scripts that you create in the LabVIEW MathScript Window. The MathScript executes LabVIEW MathScripts and your other text-based scripts using the MathScript RT Module engine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
